Best Practices of Instructional Leadership among Principals of Primary and Secondary Schools in Male’, Maldives
Submission to VIJ 2023-10-30
Keywords
- Principals’ best practices,
- instructional leadership,
- teachers’ perceptions
Copyright (c) 2023 Mohamed Shujau-Abdul-Raheem

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
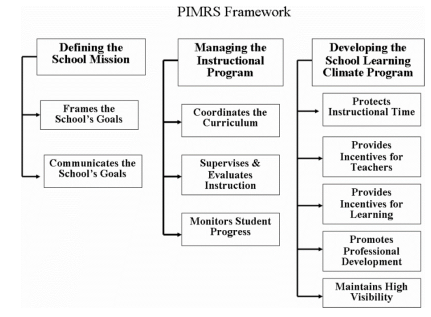
The purpose of this study was to examine the best practices of instructional leadership among principals of primary and secondary schools in Male’, Maldives, based on teachers’ perceptions. The Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale (PIMRS), developed by Hallinger and Murphy (1985) and modified by Hallinger and Wang (2015), served as the instrument for data collection through a questionnaire. A total of 392 teachers from schools in Male’, Maldives, were surveyed and data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0. The result of the study shows that all three dimensions of instructional leadership—"defining the school mission" (mean 4.05), "managing the instructional program" (mean 3.94), and "developing a positive school learning climate" (mean 3.72)—have reached a high level in practice. The study shows that the three best practices of principals in instructional leadership are to effectively communicate the school's mission to members of the school community (dimension 'Defining the School's Mission', mean 4.12), to clarify who is responsible for coordinating the curriculum across grade levels (dimension 'Managing the Instructional Program', mean 4.29), and to encourage teachers to use class time to teach and practice new skills and concepts (dimension 'Developing a Positive School Climate', mean 4.10). It is hoped that this study will provide useful insights that will be effective in improving the instructional leadership skills of principals to improve the academic performance of students and create a world-class human capital that is comparably excellent.
References
- Ahmed, A. R. (2016). Instructional Leadership Practices of Selected Principals in Maldives: A Case Study. Asia e University.
- Alig-Mielcarek, J. M. (2003). A Model of School Success: Instructional Leadership, Academic Press, and Student Achievement [The Ohio State University]. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=osu1054144000
- Bear, G. G., Yang, C., & Pasipanodya, E. (2015). Assessing School Climate: Validation of a Brief Measure of the Perceptions of Parents. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 33(2), 115–129. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282914545748
- Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational Research: Planning, Conducting, and Evaluating Quantitative and Qualitative Research (Vice President and Editor-in-Chief: Paul A. Smith & Development Editor: Christina Robb (eds.); 4th ed.). Pearson.
- Dupont, J. P. (2009). Teacher Perceptions of The Influence of Principal Instructional Leadership on School Culture: A Case Study of The American Embassy School in New Delhi, India. Unpublished Doctoral Thesis.
- Hair, J. F., Black, W. C., Babin, B. J., & Anderson, R. E. (2019). Multivariate Data Analysis. In Hampshire, UK : Cengage Learning, EMEA: Vol. 8th Ed.
- Hallinger, P. (2011). A review of three decades of doctoral studies using the principal instructional management rating scale: A lens on methodological progress in educational leadership. In Educational Administration Quarterly (Vol. 47, Issue 2). https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X10383412
- Hallinger, P., & Murphy, J. (1985). Assessing the Instructional Management Behavior of Principals. The Elementary School Journal, 86(2), 217–247. https://doi.org/10.1086/461445
- Hallinger, P., & Wang, W.-C. (2015). Assessing Instructional Leadership with the Principal Instructional Management Rating Scale. In Springer. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-15533-3
- Harris, S. L., & Lowery, S. (2002). A View from the Classroom. Educational Leadership, 59(8), 64–66.
- Hassan, R., Ahmad, J., & Boon, Y. (2018). Instructional leadership in Malaysia. International Journal of Engineering and Technology (IJET), 7(3.30 Special Issue 30), 424–432. https://doi.org/10.14419/ijet.v7i3.30.18346
- Krug, S. E. (1992). Instructional Leadership: A Constructivist Perspective. Educational Administration Quarterly, 28(3), 430–443. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X92028003012
- Landell, K. (1997). Management by menu. Wiley & Sons Inc.
- Maldives Ministry of Education. (2018). Public Finance Analysis of the Education Sector.
- Ministry of Education. (2020). Maldives Education Response Plan.
- Moffitt, J. R. (2007). What Works : Principal Leadership Behaviors that Positively Impact Student Achievement in Elementary Schools [Georgia Southern University]. https://digitalcommons.georgiasouthern.edu/etd/264
- Robinson, V. M. J., Lloyd, C. A., & Rowe, K. J. (2008). The impact of leadership on student outcomes: An analysis of the differential effects of leadership types. Educational Administration Quarterly, 44(5), 635–674. https://doi.org/10.1177/0013161X08321509
- Salleh, M. J. (2013). Best Practice of Framing and Communicating School Goals by Principals of Cluster Secondary Schools Malaysia. In International Journal of Arts and Commerce (Vol. 2, Issue 2). www.ijac.org.uk
- Salleh, M. J. (2014). Best Practice of Framing and Communicating School Goals Among Principals of Cluster Secondary Schools Towards Realization of Malaysian Education Blueprint 2013-2025. The International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Invention, 1(6), 458–466. https://www.academia.edu/40347148/Best_Practice_Of_Framing_And_Communicating_School_Goals_Among_Principals_Of_Cluster_Secondary_Schools_Towards_Realization_Of_Malaysian_Education_Blueprint_2013_2025
- Salleh, M. J., Abu Bakar, S., Prof, A., Bakar, S. A., & Journal, E. (2018). Best Practices of Promoting a Positive School Learning Climate Among Headteachers of High Performing Primary Schools and Education-Blueprint 2013-2025 Malaysia. European Journal of Education Studies, 4(0), 288. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1408859
- Salleh, M. J., & Hatta, M. (2018). Best Practices of Promoting a Positive School Learning Climate among Principals of Cluster Secondary Schools Towards Realization of Education Blueprint 2013-2025 Malaysia. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal, 5(8), 223–233.
- Salleh, M. J., & Kamaruddin, N. Z. (2020). Best Practice of Principals’ Communicating the School Goals and Evaluating Instruction in Generating Quality Teaching. European Modern Studies Journal, 4(2), 110–122. http://journal-ems.com/index.php/emsj/article/view/94/88
- Salleh, M. J., & Mitul, S. J. (2021). Incorporating Principles of Instructional Leadership in Love Pedagogy towards School Excellence: Teachers Perspectives. International Journal of Advanced Research in Education and Society, 3(4), 91–108. https://myjms.mohe.gov.my/index.php/ijares/article/view/16666/8741
- Sarok, A., & Jihet, R. (2012). The Relationship between Headmasters Instructional Leadership and Teachers Commitment. Scottish Journal of Arts, Social Sciences and Scientific Studies, 3(1), 3–26. https://www.academia.edu/8441153/The_Relationship_Between_Headmasters_Instructional
- Sukarmin, & Sin, I. (2021). School Health as the Mediator Variable: Determinants of the Principal Instructional Leadership Behavior. European Journal of Educational Research, 10(3), 1275–1286. https://doi.org/10.12973/eu-jer.10.3.1275
- Tshering, N. (2022). Influence of principal’s instructional leadership on teacher performance in secondary schools of Thimphu district, Bhutan. Bhutan Journal of Research and Development , 11(2). https://doi.org/10.17102/BJRD.RUB.11.2.034
- Walker, A. (2016). Exemplary School Principals’ Role in Teachers’ Commitment, Professional Involvement, and Innovativeness: Case Studies of Four School Principals. Memorial University.