Submission to VIJ 2024-11-13
Keywords
- Memory, Large Language Models (LLMs), Persistent Context, Conversational AI, Contextual Intelligence, Ethical AI, Memory Augmentation, Personalized Interaction, User Experience, Privacy.
Copyright (c) 2024 Valentina Porcu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
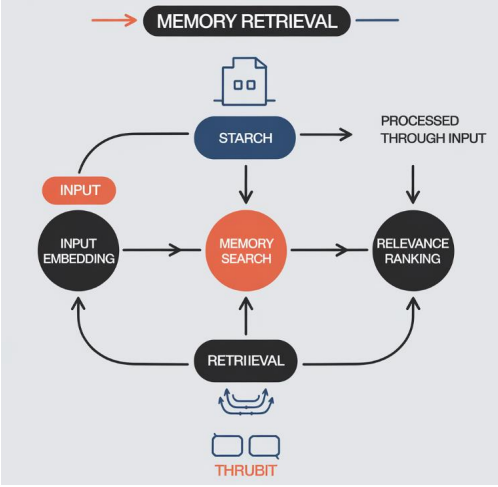
Memory in LLMs has given way to more logical and sensible interactions between the system and the user. This is different from other models that are session bound, such that the responses to any one query are not related to past and future interactions with the same user, but memory-enabled LLMs retain information across sessions and continually update interactions with the person they are communicating with. The role of permanent memory in LLMs is considered in this work, provided through the analysis of the role of memory mechanisms in maintaining conversation flows, improving user interaction, and supporting practical applications in various industries, including customer service, healthcare, and education. Discussing how the idea and architectures of memory correspond to storage and retrieval procedures and the management of memory in LLMs this paper outlines the opportunities and challenges for AI systems that want to include contextual intelligence but also remain ethical. The synthesis of important concepts underlines the promising prospects of memory-augmented models in improving the communication with users and points to the imperatively important aspect of controlling the memory process at the design stage of LLMs. We also offer recommendations for privacy and ethical concerns that should be avoided in the case of future AI memory advancements in an effort to pursue sustainable technological progress while also incorporating user-oriented values into the process.
References
- Jo, E., Jeong, Y., Park, S., Epstein, D. A., & Kim, Y. H. (2024, May). Understanding the Impact of Long-Term Memory on Self-Disclosure with Large Language Model-Driven Chatbots for Public Health Intervention. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (pp. 1-21).
- Pawar, S., Tonmoy, S. M., Zaman, S. M., Jain, V., Chadha, A., & Das, A. (2024). The What, Why, and How of Context Length Extension Techniques in Large Language Models--A Detailed Survey. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.07872.
- Johnsen, M. (2024). Large Language Models (LLMs). Maria Johnsen.
- Zheng, S., He, K., Yang, L., & Xiong, J. (2024). MemoryRepository for AI NPC. IEEE Access.
- Alawad, A., Abdeen, M. M., Fadul, K. Y., Elgassim, M. A., Ahmed, S., & Elgassim, M. (2024). A Case of Necrotizing Pneumonia Complicated by Hydropneumothorax. Cureus, 16(4).
- Chanane, F. (2024). Exploring Optimization Synergies: Neural Networks and Differential Evolution for Rock Shear Velocity Prediction Enhancement. International Journal of Earth Sciences Knowledge and Applications, 6(1), 21-28.
- Ullah, A., Qi, G., Hussain, S., Ullah, I., & Ali, Z. (2024). The role of llms in sustainable smart cities: Applications, challenges, and future directions. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.14596.
- Xu, Z., Xu, H., Lu, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhu, R., Wang, Y., ... & Shang, L. (2024). Can Large Language Models Be Good Companions? An LLM-Based Eyewear System with Conversational Common Ground. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies, 8(2), 1-41.
- Elgassim, M. A. M., Sanosi, A., & Elgassim, M. A. (2021). Transient Left Bundle Branch Block in the Setting of Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema. Cureus, 13(11).
- Miloud, M. O. B., & Liu, J. (2023, April). An Application Service for Supporting Security Management In Software-Defined Networks. In 2023 7th International Conference on Cryptography, Security and Privacy (CSP) (pp. 129-133). IEEE.
- Bastola, A., Wang, H., Hembree, J., Yadav, P., McNeese, N., & Razi, A. (2023). LLM-based Smart Reply (LSR): Enhancing Collaborative Performance with ChatGPT-mediated Smart Reply System. arXiv preprint.
- Xiong, H., Bian, J., Yang, S., Zhang, X., Kong, L., & Zhang, D. (2023). Natural language based context modeling and reasoning with llms: A tutorial. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.15074.
- MILOUD, M. O. B., & Kim, E. Optimizing Multivariate LSTM Networks for Improved Cryptocurrency Market Analysis.
- Elgassim, M. A. M., Saied, A. S. S., Mustafa, M. A., Abdelrahman, A., AlJaufi, I., & Salem, W. (2022). A Rare Case of Metronidazole Overdose Causing Ventricular Fibrillation. Cureus, 14(5).
- Yang, H., Lin, Z., Wang, W., Wu, H., Li, Z., Tang, B., ... & Weinan, E. (2024). Memory3: Language modeling with explicit memory. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.01178.
- Goertzel, B. (2023). Generative ai vs. agi: The cognitive strengths and weaknesses of modern llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.10371.
- Pillai, V. (2023). Integrating AI-Driven Techniques in Big Data Analytics: Enhancing Decision-Making in Financial Markets. Valley International Journal Digital Library, 25774-25788.
- Elgassim, M., Abdelrahman, A., Saied, A. S. S., Ahmed, A. T., Osman, M., Hussain, M., ... & Salem, W. (2022). Salbutamol-Induced QT Interval Prolongation in a Two-Year-Old Patient. Cureus, 14(2).
- Kalita, A. (2024). Large Language Models (LLMs) for Semantic Communication in Edge-based IoT Networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.20970.
- Feng, T., Jin, C., Liu, J., Zhu, K., Tu, H., Cheng, Z., ... & You, J. How Far Are We From AGI: Are LLMs All We Need?. Transactions on Machine Learning Research.
- Pillai, V. (2024). Implementing Loss Prevention by Identifying Trends and Insights to Help Policyholders Mitigate Risks and Reduce Claims. Valley International Journal Digital Library, 7718-7736.
- Yin, W., Xu, M., Li, Y., & Liu, X. (2024). Llm as a system service on mobile devices. arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.11805. Bärmann, L., DeChant, C., Plewnia, J., Peller-Konrad, F., Bauer, D., Asfour, T., & Waibel, A. (2024). Episodic Memory Verbalization using Hierarchical Representations of Life-Long Robot Experience. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.17702.Xu, Z., Xu, H., Lu, Z., Zhao, Y., Zhu, R., Wang, Y., ... & Shang, L. (2023). Can Large Language Models Be Good Companions? An LLM-Based Eyewear System with Conversational Common Ground. arXiv preprint arXiv:2311.18251.
- Elgassim, M., Abdelrahman, A., Saied, A. S. S., Ahmed, A. T., Osman, M., Hussain, M., ... & Salem, W. (2022). Salbutamol-Induced QT Interval Prolongation in a Two-Year-Old Patient. Cureus, 14(2).
- Sharma, P., & Devgan, M. (2012). Virtual device context-Securing with scalability and cost reduction. IEEE Potentials, 31(6), 35-37.
- Shoraka, Z. B. (2024). Biomedical Engineering Literature: Advanced Reading Skills for Research and Practice. Valley International Journal Digital Library, 1270-1284.
- Ramey, K., Dunphy, M., Schamberger, B., Shoraka, Z. B., Mabadeje, Y., & Tu, L. (2024). Teaching in the Wild: Dilemmas Experienced by K-12 Teachers Learning to Facilitate Outdoor Education. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference of the Learning Sciences-ICLS 2024, pp. 1195-1198. International Society of the Learning Sciences.
- Liu, Z., Wang, J., Dao, T., Zhou, T., Yuan, B., Song, Z., ... & Chen, B. (2023, July). Deja vu: Contextual sparsity for efficient llms at inference time. In International Conference on Machine Learning (pp. 22137-22176). PMLR.
- Chen, Y., & Xiao, Y. (2024). Recent advancement of emotion cognition in large language models. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.13354.
- Wasserkrug, S., Boussioux, L., & Sun, W. (2024). Combining Large Language Models and OR/MS to Make Smarter Decisions. In Tutorials in Operations Research: Smarter Decisions for a Better World (pp. 1-49). INFORMS.
- Shoraka, Z. B. (2024). Biomedical Engineering Literature: Advanced Reading Skills for Research and Practice. Valley International Journal Digital Library, 1270-1284.
- Zhong, W., Guo, L., Gao, Q., Ye, H., & Wang, Y. (2024, March). Memorybank: Enhancing large language models with long-term memory. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 38, No. 17, pp. 19724-19731).
- Guo, J., Li, N., Qi, J., Yang, H., Li, R., Feng, Y., ... & Xu, M. (2023). Empowering Working Memory for Large Language Model Agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2312.17259.
- Zhang, K., Zhao, F., Kang, Y., & Liu, X. (2023). Memory-augmented llm personalization with short-and long-term memory coordination. arXiv preprint arXiv:2309.11696.
- Ramey, K., Dunphy, M., Schamberger, B., Shoraka, Z. B., Mabadeje, Y., & Tu, L. (2024). Teaching in the Wild: Dilemmas Experienced by K-12 Teachers Learning to Facilitate Outdoor Education. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference of the Learning Sciences-ICLS 2024, pp. 1195-1198. International Society of the Learning Sciences.
- Fountas, Z., Benfeghoul, M. A., Oomerjee, A., Christopoulou, F., Lampouras, G., Bou-Ammar, H., & Wang, J. (2024). Human-like episodic memory for infinite context llms. arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.09450.
- Zhang, Z., Bo, X., Ma, C., Li, R., Chen, X., Dai, Q., ... & Wen, J. R. (2024). A survey on the memory mechanism of large language model based agents. arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.13501.
- Sun, R. (2024). Can A Cognitive Architecture Fundamentally Enhance LLMs? Or Vice Versa?. arXiv preprint arXiv:2401.10444.
- Jiang, Y., Rajendran, G., Ravikumar, P., & Aragam, B. (2024). Do LLMs dream of elephants (when told not to)? Latent concept association and associative memory in transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.18400.
- Sun, R. (2024). Roles of LLMs in the Overall Mental Architecture. arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.20037.
- Shang, J., Zheng, Z., Wei, J., Ying, X., Tao, F., & Team, M. (2024). Ai-native memory: A pathway from llms towards agi. arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.18312.
- Ko, C. Y., Dai, S., Das, P., Kollias, G., Chaudhury, S., & Lozano, A. (2024, December). MemReasoner: A Memory-augmented LLM Architecture for Multi-hop Reasoning. In The First Workshop on System-2 Reasoning at Scale, NeurIPS'24.
- Karakolias, S., Kastanioti, C., Theodorou, M., & Polyzos, N. (2017). Primary care doctors’ assessment of and preferences on their remuneration: Evidence from Greek public sector. INQUIRY: The Journal of Health Care Organization, Provision, and Financing, 54, 0046958017692274.
- Karakolias, S. E., & Polyzos, N. M. (2014). The newly established unified healthcare fund (EOPYY): current situation and proposed structural changes, towards an upgraded model of primary health care, in Greece. Health, 2014.
- Dixit, R. R. (2021). Risk Assessment for Hospital Readmissions: Insights from Machine Learning Algorithms. Sage Science Review of Applied Machine Learning, 4(2), 1-15.
- Dixit, R. R. (2021). Risk Assessment for Hospital Readmissions: Insights from Machine Learning Algorithms. Sage Science Review of Applied Machine Learning, 4(2), 1-15.
- Polyzos, N. (2015). Current and future insight into human resources for health in Greece. Open Journal of Social Sciences, 3(05), 5.
- Dixit, R. R. (2021). Risk Assessment for Hospital Readmissions: Insights from Machine Learning Algorithms. Sage Science Review of Applied Machine Learning, 4(2), 1-15.