Algorithm for Prevention of Recurrent Pregnancy Loss and Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in Patient with Inherited Thrombophilia
Submission to VIJ 2024-08-21
Abstract
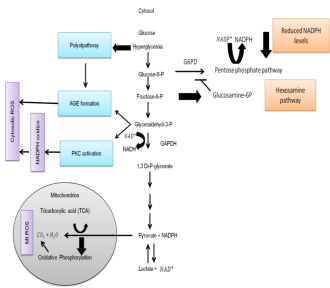
Pregnancy-related complications such as recurrent pregnancy loss, recurrent implantation failure, preeclampsia, intrauterine fetal growth restriction, and gestational diabetes pose significant risks to both maternal and fetal health. Emerging evidence suggests that genetic variations may contribute to the etiology of many of these conditions.
Understanding the interplay between genetic mutations and pregnancy complications can enhance risk assessment and enable personalized medical management for affected individuals. Further research is needed to better elucidate these relationships and guide clinical decision-making.
The objective of this study is to emphasize the medical implications of detecting congenital abnormalities in pregnant women and to underscore the importance of risk prediction, early diagnosis, and personalized care in improving maternal and fetal health outcomes. This comprehensive analysis underlines the critical role of algorithms in preventing severe pregnancy-related complications and enhancing targeted interventions in obstetric care. By elucidating the intricate pathogenesis of these conditions, the study provides valuable insights for improving specific therapeutic approaches.