The Effect of Crime on Foreign Investment and Economic Development in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Panel Data Analysis
Submission to VIJ 2024-07-28
Keywords
- Panel VAR model, Impulse response, Variance decomposition, Causality test
Copyright (c) 2024 Yakubu Musa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
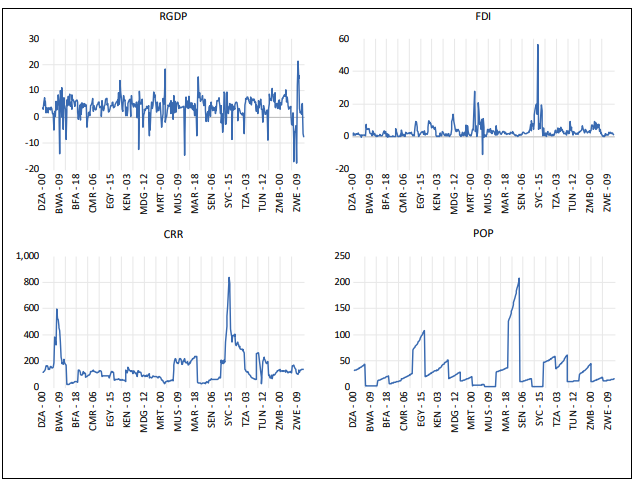
This study investigates the effect of crime on economic development in 22 sub-Saharan African countries between 2000 and 2020, using data from global sources. The study utilized a panel vector autoregression (VAR) approach to analyze the dynamic correlations between variables. This was achieved through the examination of impulse response functions and error variance decomposition. The study established a definitive cause-and-effect connection between the crime rate and growth indicators. The panel vector autoregression (VAR) technique resolves the issue of endogeneity by permitting endogenous interaction among the variables in the system. The findings indicate that the crime rate has a significant effect on economic growth in sub-Saharan countries, though with very low magnitude. The economic prosperity of most sub-Saharan African countries may be attributed to the abundant availability of natural resources in the region. The causality test findings indicate a diverse causal connection between the crime rate and growth indicators. While there is no direct causal relationship between economic growth and the crime rate, there is a one-way causality between economic growth and foreign investment. This means that economic growth can enhance foreign investment, suggesting that in sub-Saharan countries, economic growth plays a crucial role in improving foreign investment. However, as indicated by the findings, there exists a bidirectional causal relationship between foreign investment and crime rates. In summary, it is clear that the crime rate in sub-Saharan African nations has a significant impact. In the future, countries with higher crime rates are likely to see slow economic growth and less foreign investment.
References
- Ahmad, A, Ali S. & Ahmad, N. (2014). Crime and economic growth in developing countries: Evidence from Pakistan. Journal of Basic and Applied Scientific Research, 4(4), 31-41. Retrieved from www.textroad.com
- Amat Adarov (2019). Dynamic Interactions Between Financial and Macroeconomic Imbalances: A
- Panel VAR Analysis. Working Paper 162. The Vienna Institute for International Economic Studies
- Ayang Eric, Timbi Sézard, and Toumpiguim Missa Daniel (2021). Effects of Unemployment on Crime in selected Sub-Sahara African countries. International Journal of Scientific Research and Management. Volume 09 Issue 02.
- Becker, G. S. (1968). Crime and punishment: An economic approach. In The economic dimensions of crime (p. 13 68). Springer.
- Breitung, J. (2000), “The local power of some unit root tests for panel data”, in Baltagi, B.H., Fomby,
- T.B.,Hill, R.C. (Eds), Nonstationary Panels, Panel Cointegration, and Dynamic Panels (Advances in Econometrics, Volume 15), Elsevier Science, pp. 161-178
- Domingo, Sammy (2023) Describing the Effects of Unemployment on the Increase of Violence and Crime in Africa. Thesis, De La Salle University – Dasmariñas .
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/367339272
- Enders, W., 2014. Applied Econometric Times Series. NY, John Wiley & Sons, New York.
- Granger, C.W.J., (1969). Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross spectral methods. Econometrica 37 (3), 424–438. https://doi.org/10.2307/1912791.
- Hadri, K. (2000), “Testing for stationary in heterogeneous panel data”, Econometrics Journal, Vol. 3,pp. 148-161.
- Im, K., Pesaran, H., and Shin, Y. (2003). Testing for Unit Roots in Heterogeneous Panels. Journal of Econometrics, 115:53–74.
- Levin, A., C. Lin, and C.J. Chu (2002), Unit Root Tests in Panel Data: Asymptotic and Finite-sample Properties, Journal of Econometrics, 108, 1{24.
- Maddala, G. S., & Wu, S. (1999). A comparative study of unit roots with panel data and a new simple test. Oxford Bulletin of Economics and Statistics, 61, 631–651
- Mary Yaya Kenfoy & Minko Ella Annie (2016) An Overview of Crime in Sub-Saharan Africa in the 21st Century. Research Journal of Commerce & Behavioral Science, Volume: 05, Number: 07.
- Metu, A. Kalu, U. C & Ezenekwe, R.U. (2013). Demographic pattern and sustainable development in Nigeria. In
- A. C. Mbanefo, & Au. N. Nnonyelu, (Eds.) Challenges of sustainable development: A social science approach (pp.124-140). Awka: Fab Anieh Nig.
- Musa Y. and Jibrin A. Sanusi (2013). Analyzing the impact of Value Added Tax (VAT) on Economic Growth in Nigeria. Journal of Mathematical Theory and Modeling. Vol.3(14); PP:16- 23.
- Pranav Raj & Siva Reddy Kalluru (2023) Does crime impede economic growth? An evidence from India, Cogent Social Sciences, 9:1, 2196814, DOI: 10.1080/23311886.2023.2196814
- Tassew Dufera Tolcha, Svein Bråthen, and Johan Holmgren (2020). Air transport demand and economic development in sub-Saharan Africa: Direction of causality. Journal of Transport Geography. Volume 86, June 2020, 102771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtrangeo.2020.102771
- World Bank (Washington, U. (2006). Global Development Finance 2006: The Development Potential of Surging Capital Flows. Review, analysis, and outlook. I. World Bank.
- Yakubu Musa, Asare, B. K., and Gulumbe, S.U. (2013). Effect of Monetary-Fiscal Policies Interaction on Price and output Growth in Nigeria. CBN Journal of Applied Statistics. Vol. 4(1): 55-75