Development of Multiplechoice Test Instruments to Improve Scientific Literacy in Madrasah Aliyah (MA)
Submission to VIJ 2024-06-29
Keywords
- scientific literacy,
- instrument,
- validity ,
- level of difficulty,
- discrimination power
Copyright (c) 2024 Sudirman, Ani Rusilowati , Endang Susilaningsih

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
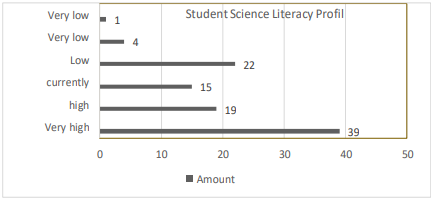
The ability to analyze and interpret scientific information is very important in the era of advanced technology. For Madrasah Aliyah (MA) students, scientific literacy is crucial for academic and future achievements, including understanding scientific concepts, interpreting data, making decisions, and communicating scientific ideas. Although scientific literacy is important, many MA students face challenges due to traditional teaching methods and inappropriate assessment. This research aims to develop and measure a multiplechoice test instrument for MA students' scientific literacy, empirically validated to improve science education and prepare students to face the modern world. Research and development (research and development) with 3D models (Define, Design, Development). Focus on scientific literacy questions with PISA indicators. Overall, it shows that the instruments used are very good and valid, and provide a positive picture of students' scientific literacy abilities, although there are still certain areas that need to be improved. Questions with poor power differences need to be repaired or replaced, and questions with sufficient power differences need to be revised. Low scores in explaining scientific phenomena require additional guidance. Regular monitoring and revision is important to maintain the quality of the instrument. This instrument is valid and reliable, but continuous improvement is needed.
References
- Arikunto;, S. (2015). Research procedures a practical approach (Jakarta). Rineka Cipta.
- Arikunto, S. (2018). Basics of Educational Evaluation (R. Damayanti (ed.). Jakarta: PT. Bumi Aksara.
- Barus, R.A., Rusilowat, A., & Ridlo, S. (2024). Analysis of Needs for Development of TIMSS-Oriented Science Literacy Assessment Test Instruments for Class V Elementary School Students. JP2SD (Journal of Elementary School Thought and Development), 12 (1), 68–85.
- Bórquez-Sánchez, E. (2024). Literasi sains dalam biologi dan sikap terhadap sains dalam sistempendidikan Chili. Penelitian dalam Pendidikan Sains & Teknologi, 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/02635143.2024.2320104
- Chasanah, N., Widodo, W., & Suprapto, N. (2022). Development of a Science Literacy Assessment Instrument to Describe Student Profiles. PENDIPA Journal of Science Education, 6(2), 474–483. https://doi.org/10.33369/pendipa.6.2.474-483
- Cohen, R. J. & Swerdlik, M. E. (2005). Psychological Testing and Assessment: An Introduction to Tests and Measurement ((6th ed.)). McGraw-Hill.
- Cronbach, L. J. (1970). Essentials of Psychological Testing. New York: Harper & Row.
- Harlen, W., & Qualter, A. (2004). The teaching of science in primary schools (4th ed). David Fulton.
- Kristyowati, R., & Purwanto, A. (2019). Learning Scientific Literacy Through Using the Environment. Scholaria: Journal of Education and Culture, 9(2), 183–191. https://doi.org/10.24246/j.js.2019.v9.i2.p183-191
- Lave, J., & Wenger, E. (1991). Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation (1st ed.). Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511815355
- Linn, R.I. & Gronlund, N.E. (2000). Measurement and Assessment in Teaching. Prentice Hall.
- OECD. (2016). PISA 2015 Results (Volume I): Excellence and Equity in Education. OECD. https://doi.org/10.1787/9789264266490-en
- Ojimba, D.P. (2013). Scientific and Technological Literacy In Africa: Issues, Problems And Prospects' Dimensions (IPP). Educational Research International, 2(1).
- Pertiwi, U.D., Atanti, R.D, & Ismawati, R. (2018). The Importance of Scientific Literacy In 21st Century Smp School Science Learning. Indonesian Journal of Natural Science Education (IJNSE), 01 (01), 24–29.
- Pratiwi, S.N., Cari, C.., & Aminah, N.S. (2019). 21st Century Science Learning with Students' Scientific Literacy. Journal of Physics Materials and Learning (JMPF), 9 (1).
- Purwanto. (2009). Evaluation of learning outcomes. Student Library.
- Ridwan et al. (2013). Development of a Student Scientific Literacy Test Instrument on the Topic of Diversity of Living Creatures. Journal of Biology Education and Learning, 4(1), 71–78.
- Septiani, D., Rizky, F. Y., Latifah, N., Suhani, S., & Hayashi, T. E. (2020, January 13). Analysis of Reading Comprehension Ability in Explanatory Texts in Class XI Science 5 Students of SMA Negeri 5 Karawang 2019/2020 Academic Year.
- Singer, S. R., Nielsen, N. R., & Schweingruber, H. A. (2012). Discipline-based education research: Understanding and improving learning in undergraduate science and engineering. The National academies press.
- Sugiyono. (2015). Educational research methods include quantitative, qualitative and R&D approaches. (Cet. 21). Alphabet.
- Sujarweni, V., W. (2014). Research methodology: Complete, practical, and easy to understand. New press library.
- Thiagarajan, S. (1974). Instructional Development for Training Teachers of Exceptional Children: A Sourcebook. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:148925881
- Thurstone, L.L. (1929). Theory of attitude measurement: Vol. 36(3). Psychological Review.
- Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in Society: The Development of Higher Psychological Processes (M. Cole, V. John-Steiner, S. Scribner, & E. Souberman, Eds.; Revised ed. edition). Harvard University Press.
- Widoyoko, E.K. (2012). Techniques for preparing research instruments. Student Son.