Submission to VIJ 2024-05-03
Keywords
- Influential factors,
- entrepreneurship,
- Gen Z,
- Vietnamese youth.
Copyright (c) 2024 Thanh Tung Hoang, Phan Ha Thy

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
To investigate the factors influencing the entrepreneurship intention of generation Z youths in Vietnam, the research team utilized a quantitative research method which base on data from a survey of 353 Vietnamese youths, of which 311 were either currently involved in entrepreneurship, preparing for entrepreneurship, or intending to engage in entrepreneurship. Using the SMARTPLS software, the study found that, with a confidence level of 95%, “Perceived behavioral control” (PBC) had the strongest impact on the e-entrepreneurship intention of Vietnamese generationZ, with an influence level of 0.439. Following this, the “Social influence” (SIN) factor demonstrated a significant impact of 0.224. At a confidence level of 90%, the “Expectation of success” (EXSU) factor showed an influence of 0.126, while the “Attitude towards E- entrepreneurship” (ATTE) factor exhibited an influence of 0.089. Additionally, the “Entrepreneurship education” (EDED) and “Entrepreneurship competence” (ENTC) factors did not yield statistically significant results regarding their influence on the dependent variable, “E-entrepreneurship iIntention of Vietnamese generation Z” (EEINT). Based on research results, the research team proposed discussions aimed at promoting and supporting youths to enhance the effectiveness of their electronic entrepreneurship projects
References
- Ajzen, (1985), From intention to actions: A theory of planned behaviior, Springer, New York
- Ajzen, I. (1991), The theory of Planned Behavior, organizational Behavior and human decision processes, 50, 179-211
- Alex Smith (2019). What Are The Core Challenges In E-Entrepreneurship? https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-core-challenges-e-entrepreneurship-alex-smith
- Anagnoste, Sorin, and Petronela Cirstea (2023). Young, Wild & Entrepreneurship: Generation Z’s Affinity for Entrepreneurship.
- www.researchgate.net/publication/372443196_Young_Wild_Entrepreneurship_Generation_Z’s_Affinity_for_Entrepreneurship.
- Bagozzi, R. and Yi, Y (1988). On the Evaluation of Structural Equation Models. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Sciences, 16, 74-94. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/BF02723327
- Bird, B. (1988). Implementing Entrepreneurship Ideas: The Case for Intention. Academy of Management Review, 13, 442-454.
- Canses Tican (2019). Pre-Service Primary School and Pre-School Teachers’ Perception of Individual Entrepreneurship and Opinions about Their Creative Thinking Tendency. International Journal of Educational Methodology, Volume 5, Issue 4, 591 - 606.
- Chin, W. W. (1998). The partial least squares approach for structural equation modeling. In G. A. Marcoulides (Ed.), Modern methods for business research (pp. 295–336). Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
- Clark, L. A., & Watson, D. (1995). Constructing validity: Basic issues in objective scale development. Psychological Assessment, 7(3), 309–319. https://doi.org/10.1037/1040-3590.7.3.309
- Compeau Z., Higgins C. (1995), Application of social cognitive theory to training for computer skills, Information systems research, 6 (2) 118-143.
- Comrey, A.L, & Lee, H. B. (1992). A First Course in Factor Analysis (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum.
- Cohen, J. (1988). Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (2nd ed.). Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Publishers.
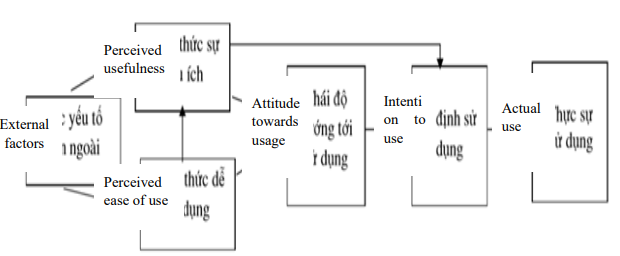
- David, (1989), Perceived usefulness, pervceived ease of use and user acceptance of information technology, MIS quarterly, 13 (3), 319-339
- Davis, F.D., Bagozzi, R.P., Warshaw, P.R. (1992), Extrinsic and intrinsic motivationtousecomputers intheworkplace. J.Appl.Soc. Psychol. 22(14), 11– 32
- Devellis, R (2012). Scale Development Theory and Applications. Sage Publications, New York.
- Do Thi Hoa Lien (2021). Factors affecting the readiness to start a business of graduates in Business Administration: case study at the University of Labor and Social Affairs (Ho Chi Minh City campus). Hue University Science Magazine: Economics and Development; pISSN: 2588–1205; eISSN: 2615–9716; Issue 131, No 5C, 2022, pp. 5–24, DOI: 10.26459/hueunijed.v131i5C.6522
- Elaine (2023). Unleashing the Power of Technology: Discovering the Benefits of E-Entrepreneurship. Bost Innovation,5Dec.2023, bostinnovation.com/unleashing-the-power-of-technology-discovering-the-benefits-of-e-entrepreneurship/. Accessed 10 Dec. 2023.
- Fishbein and Ajzen (1975), Belief, attitude, intention and behavior: An introduction to theory and research, Addison- Wesley, Reading, MA
- Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18(1), 39–50. https://doi.org/10.2307/3151312
- Felix, M., and Dasuni Pandithasekara (2022). Factors Affecting the E-Entrepreneurship intention among generation Z of Sri Lanka. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, 16 Sept. 2022, pp. 767–779, https://doi.org/10.55248/gengpi.2022.3.9.17.
- Garson, G.D (2016). Partial Least Squares: Regression and Structural Equation Models. Statistical Associates Publishers, Asheboro.
- Greve, A., Salaff J.W., (2003). Social Networks and Entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice 28(1):1 – 22
- Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Babin, B. J., & Black, W. C. (2010). Multivariate data analysis: A global perspective. Pearson Education, London.
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2016). A primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) (1st ed.). Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage publications.
- Hair, J. F., Hult, G. T. M., Ringle, C. M., Sarstedt, M., & Thiele, K. O (2017). A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) (2nd ed.). SAGE Publications.
- Hartwick, J., & Barki, H. (1994), Explaining the role of user participation in information system use, Management Science, 40(4), 440-465.
- Henseler, J. and Sarstedt, M (2013). Goodness-of-Fit Indices for Partial Least Squares Path Modeling. Computational Statistics, 28, 565-580. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00180-012-0317-1
- Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2015). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115-135.
- Herrero Crespo & Rodriguez Del Bosque (2010), Effect of perceived risk on e-commerce acceptance, State of the art and future research directions.
- Hien Vo & et al (2021). Research on factors affecting entrepreneurial intention of students at Tien Giang University. DOI:10.46223/HCMCOUJS.econ.vi.16.2.578.2021
- Hoang Thanh Tung, Nguyen Thi Van Anh, Doan Thi Mai Huong, Tang Anh Cuong (2023). Factors affecting the readiness to start a business of students majoring in Business Administration at the University of Labor and Social Affairs. Proceedings of the national scientific conference "Promoting startups and innovation in the context of digital transformation". Finance Publishing House
- Hoang Trong, Chu Nguyen Mong Ngoc (2005). Analyze research data with SPSS. Statistics Publishing House.
- Huston, Heather (2023). Starting a Business as a Gen Z Entrepreneur. Www.wolters kluwer.com, 1 June 2023,
- Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff Criteria for Fit Indexes in Covariance Structure Analysis: Conventional Criteria versus New Alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling, 6, 1-55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/10705519909540118
- Hock, C., Ringle, C.M., & Sarstedt, M (2010). Management of multi-purpose stadiums: Importance and performance measurement of service interfaces. International Journal of Services Technology and Management, 14(2-3)
- Hidayah, N. (2022). Factors affecting entrepreneurship intention of generation Z using the e-commerce platform: Evidence from Indonesia. International Journal of Business, Economics and Law, vol. 27, no. 1, Aug. 2022, p. 1, ijbel.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/09/IJBEL27.ISU1_219.pdf.
- Kline, R. B. (2015). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modeling. Guildford Press.
- Koe, W. L. (2016). The relationship between Individual Entrepreneurship Orientation (IEO) and entrepreneurship intention. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 6(1), 13
- Kolvereid Lars (1996). Prediction of Employment Status Choice Intention. Volume 21, Issue 1
- Kollmann, Tobias (2006). What is E-Entrepreneurship? Fundamentals of company founding in the net economy. January 2006International Journal of Technology Management 33(4). DOI:10.1504/IJTM.2006.009247
- Khoi Nghiep Tre (2021). Youth Entrepreneurship: What are the Advantages and Difficulties? – Young Entrepreneurs – Startup & Business Management Website. khoinghieptre.vn/van-de-khoi-nghiep-cua-gioi-tre/. Accessed 30 Dec. 2023.
- Lau, V. P., Dimitrova, M. N., Shaffer, M. A., Davidkov, T., & Yordanova, D. I. (2012). Entrepreneurship readiness and firm growth: an integrated etic and emic approach. Journal of International Management, 18(2), 147–159. doi:10. 1016/j.intman.2012.02.005
- Liñán, F., & Chen, Y. W. (2009). Development and Cross–Cultural Application of a Specific Instrument to Measure Entrepreneurship Intention. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 33(3), 593-617. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-6520.2009.00318.x
- Lowell W.B. et al, (2003). Entrepreneurship Research in Emergence: Past Trends and Future Directions. Journal of Management, Vol. 29 No. 3, pp. 285-308, 2003
- Marian Felix & et al (2022). Factors Affecting the E-entrepreneurship Intention among Generation Z of Sri Lanka. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews, Vol 3, no 9, pp 767-779, September 2022
- Mai Thi Dung, Nguyen Thi Huong, Trinh Khanh Chi (2023). Assessing the entrepreneurial capacity of students majoring in Business Administration at the University of Labor and Social Affairs. Proceedings of the national scientific conference "Promoting startups and innovation in the context of digital transformation". Finance Publishing House
- Meeyland.com (2023). What is an e-Startup? Popular Electronic Startup Model. meeyland.com/tin-tuc/khoi-nghiep-dien-tu-la-gi-mo-hinh-khoi-nghiep-dien-tu-pho-bien-376181855. Accessed 10 Dec. 2023.
- Moore G., Benbasat I. (1991), Development of instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting information technology innovation, Information systems research, 2 (3) 192-222
- Nguyen Anh Tuan (2018). Factors affecting young people's entrepreneurial intentions in Vietnam. https://khoahoc.neu.edu.vn
- Nguyen Thanh Hung & et al (2016). Factors affecting the entrepreneurial intention of students at Tra Vinh University. Scientific magazine of Tra Vinh UniversityNguyen Thi Van Anh & Tran Dan Khanh (2023). Factors affecting the entrepreneurship readiness of generation Z in Hanoi city. International Journal of Social Science and Economic Research. ISSN: 2455-8834 Volume:08, Issue:07 “July 2023”. DOI: 10.46609/IJSSER.2023.v08i07.001 URL: https://doi.org/10.46609/IJSSER.2023.v08i07.001
- Nguyen Thi Van Anh (2022). Factors affecting the implementation of digital transformation in small and medium-sized enterprises in Hanoi city. Topic at the University of Labor and Social Affairs
- Nguyen Thi Van Anh & et al (2023). The factors affecting digital transformation in small and medium enterprises in Hanoi city. Uncertain Supply Chain Management 11 (2023) 1705–1718. doi: 10.5267/j.uscm.2023.6.019
- Nurul Hidaya & et al (2022). Correlation Between Learning Styles And Academic Achievement Correlation Between Learning Styles And Academic Achievement -Nurul Hidayah. December 2022Jurnal Pendidikan Sains Sosial dan Agama 8(2). DOI:10.53565/pssa.v8i2.534
- Omsoftware (2019). What Are the Core Challenges in E-Entrepreneurship? www.omsoftware.net/technology-blog/what-are-the-core-challenges-in-e-entrepreneurship/. Accessed 30 Dec. 2023.
- Samar Alzamel & et al (2020). Factors Influencing E-Entrepreneurship Intention among Female Students in Saudi Arabia. December 2020International Journal of Criminology and Sociology 9:1996-2003. DOI:10.6000/1929-4409.2020.09.234. LicenseCC BY-NC 4.0
- Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Joseph F. Hair (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Handbook of Market Research. Springer International Publishing
- Shih, Y., Fang, K., (2004). The use of a decomposed theory of planned behavior to study Internet banking in Taiwan. Internet Research, Vol. 14 Issue: 3, pp.213-223
- Shih, H., (2004), Extendedtechnologyacceptancemodelofinternet utilization behavior. Inf. Manag. 41(6), 719–729 (2004)
- Smith, Alex (2019). What Are the Core Challenges in E-Entrepreneurship? Www.linkedin.com, 17 Nov. 2019, www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-core-challenges-e-entrepreneurship-alex-smith. Accessed 10 Dec. 2023.
- Taylor, S., Todd, P. (1995), Understandinginformationtechnology usage: a test of competing models, Inf. Syst. Res. 6(2), 144–176
- Thompson R., Higgins C., Howell J. (1991), Personal computing: Toward a conceptual model of utilization, MIS quarterly, 15 (1) 125-143
- Truong Hoang Diep Huong, Pham Duc Hien, Tran Ngoc Lam, Nguyen Thanh Thai, Nguyen Thi Thu Huong (2021). Research on factors affecting the intention to start a business of students majoring in economics in Hanoi City. Banking Science & Training Magazine No. 236+237 - January & February 2022.
- Venkatesh, V., and F.D. Davis (2000). A Theoretical Extension of the Technology Acceptance Model: Four Longitudinal Field Studies. Management Science46(2), pp. 186-204
- Viswanath Venkatesh, Michael G. Moris, Gordon B. Davis, và Fred D (2003), User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View, September 2003, MISQuarterly 27(3):425-478, DOI:10.2307/30036540
