Pragmatic critical realism and Mixed methods in Inter-disciplinary Research—Management and Information systems
Submission to VIJ 2024-03-02
Keywords
- Pragmatic Critical Realism, multidisciplinary, mixed method, management, cybersecurity, information system.
Abstract
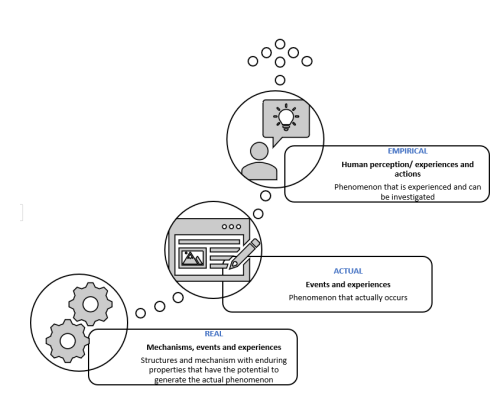
Mixed methods research traditionally follows one paradigm based on established typologies. However, this study deviates from conventional research paradigms by combining two paradigms in one study. Specifically, it employs a critical realist method to analyze data, complemented by a pragmatist approach. This combination allows for the exploration of various phenomena in multidisciplinary research, such as cyber risk management, which intersects with management and information systems. By delving into the causal mechanisms underlying observed social and organizational phenomena, the pragmatic critical realism (PCR) approach, in conjunction with mixed methods research (MMR), offers a valuable framework for understanding the study's findings. Importantly, PCR has not been widely discussed or adopted in a multidisciplinary context for examining mixed data and advancing theory using MMR. This approach can be applied to multidisciplinary research in different contexts, enabling a deeper understanding of research participants' perspectives, the observable events resulting from those perspectives, and their causal relationships. The study systematically reviews the literature on pragmatism and critical realism in the field of management and information system; compares and combines these two research paradigms to identify common ground and explore their potential for developing a new framework to address interdisciplinary research questions. As a result, a new multiparadigm conceptual model has been established that integrates pragmatism and critical realism, making an original contribution to the field of mixed methods research. The study suggests that academics and researchers in management and information systems should broaden their use of methodologies and embrace interdisciplinary thinking in order to advance theoretical debates within their discipline.
References
- Allmark, P., Machaczek, K., 2018. Realism and Pragmatism in a mixed methods study. Journal of Advanced Nursing 74, 1301–1309. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.13523
- Benbasat, I., Weber, R., 1996. Research Commentary: Rethinking ``Diversity’’ in Information Systems Research. Information Systems Research 7, 389–399.
- Bhaskar, R., 2008. A realist theory of science, Classical texts in critical realism. Routledge, London ; New York.
- Bhaskar, R., 1997. On the Ontological Status of Ideas. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour 27, 139–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-5914.00031
- Biesta, G., 2010. How to Use Pragmatism Pragmatically? Suggestions for the Twenty-First Century. Education and Culture 25. https://doi.org/10.1353/eac.0.0038
- Creswell, J.W., Clark, V.L.P., 2007. Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. SAGE.
- Dobson, P., Gengatharen, D., Fulford, R., Barratt-Pugh, L., Bahn, S., Larsen, A.-C., 2013. (PDF) Eureka moments in research: Exploring abductive processes using four case examples [WWW Document]. ResearchGate. URL https://www.researchgate.net/publication/258505608_Eureka_moments_in_research_Exploring_abductive_processes_using_four_case_examples (accessed 12.25.23).
- Downward, P., Mearman, A., 2007. Retroduction as mixed-methods triangulation in economic research: reorienting economics into social science. Cambridge Journal of Economics 31, 77–99.
- Edwards, P., 2006. Industrial Relations and Critical Realism: IR’s Tacit Contribution.
- Elder-Vass, D., 2022. Pragmatism, critical realism and the study of value [WWW Document]. URL https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/14767430.2022.2049088?needAccess=true (accessed 9.23.23).
- Feilzer, M., 2010. Doing Mixed Methods Research Pragmatically: Implications for the Rediscovery of Pragmatism as a Research Paradigm. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 4, 6–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558689809349691
- Giardina, M., 2017. (Post?)qualitative inquiry in sport, exercise, and health: notes on a methodologically contested present. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health 9, 258–270. https://doi.org/10.1080/2159676X.2016.1273904
- Heeks, R., Ospina, A.V., Wall, P.J., 2019. Combining Pragmatism and Critical Realism in ICT4D Research: An e-Resilience Case Example, in: Nielsen, P., Kimaro, H.C. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies for Development. Strengthening Southern-Driven Cooperation as a Catalyst for ICT4D, IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 14–25. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-19115-3_2
- Heeks, R., Wall, P.J., 2018. Critical Realism and ICT4D Research, in: Choudrie, J., Islam, M.S., Wahid, F., Bass, J.M., Priyatma, J.E. (Eds.), Information and Communication Technologies for Development, IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 159–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59111-7_14
- Henfridsson, O., Bygstad, B., 2013. The Generative Mechanisms of Digital Infrastructure Evolution. MIS Quarterly 37, 907–931.
- Hurrell, S.A., 2020. Critical Realism and Mixed Methods Research 25.
- Jagosh, J., 2020. Retroductive theorizing in Pawson and Tilley’s applied scientific realism [WWW Document]. URL https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/14767430.2020.1723301?needAccess=true (accessed 12.25.23).
- Johnson, P., Duberley, J., 2000. Understanding Management Research: An Introduction to Epistemology. SAGE.
- Joseph, J., 1998. In Defence of Critical Realism. Capital & Class 22, 73–106. https://doi.org/10.1177/030981689806500107
- Kasirye, F., 2021. An Overview of Mixed and Multi Method Research. https://doi.org/10.31124/advance.14681643.v1
- Kaushik, V., Walsh, C.A., 2019. Pragmatism as a Research Paradigm and Its Implications for Social Work Research. Social Sciences 8, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci8090255
- Korczynski, M., 2002. Human Resource Management in Service Work.
- Lipscomb, M., 2011. Critical realism and realist pragmatism in mixed methods: Problematics of event identity and abductive inference (evolving paradigms in mixed methods research) - Paper kindly presented on Dr Lipscomb’s behalf.
- McAvoy, J., Butler, T., 2018. A critical realist method for applied business research. Journal of Critical Realism 17, 160–175. https://doi.org/10.1080/14767430.2018.1455477
- Mearns, L., 2011. Pragmatic critical realism: Could this methodological approach expand our understanding of employment relations? Work (Reading, Mass.) 38, 359–67. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-2011-1139
- Meyer, S.B., Lunnay, B., 2013. The Application of Abductive and Retroductive Inference for the Design and Analysis of Theory-Driven Sociological Research. Sociological Research Online 18, 86–96. https://doi.org/10.5153/sro.2819
- Mingers, J., 2004. Real-izing information systems: critical realism as an underpinning philosophy for information systems. Information and Organization 14, 87–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.infoandorg.2003.06.001
- Mingers, J., 2001. Combining IS Research Methods: Towards a Pluralist Methodology. Information Systems Research 12, 240–259. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.12.3.240.9709
- Mingers, J., (2004) Future Directions in management science modelling: critical realism and multimethodology in S. Fleetwood and S. Ackroyd (eds) Critical Realist Applications in Organisation and Management Studies Routledge, London
- Morgan, D., 2014. Pragmatism as a Paradigm for Social Research. Qualitative Inquiry 20, 1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1177/1077800413513733
- Mukumbang, F., 2021. Retroductive Theorizing: A Contribution of Critical Realism to Mixed Methods Research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 17, 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/15586898211049847
- Parker, M., Mchugh, G., 1991. Five Texts in Search of an Author: A Response to John Hassard’s “Multiple Paradigms and Organizational Analysis.” Organization Studies - ORGAN STUD 12, 451–456. https://doi.org/10.1177/017084069101200306
- Phillips, E.M., Pugh, D.S., 2010. How to get a PhD: a handbook for students and their supervisors [WWW Document]. URL http://www.pdfdrive.com/how-to-get-a-phd-a-handbook-for-students-and-their-supervisors-5th-edition-d188836523.html (accessed 12.26.20).
- Phoenix, C., Osborne, N.J., Redshaw, C., Moran, R., Stahl-Timmins, W., Depledge, M.H., Fleming, L.E., Wheeler, B.W., 2013. Paradigmatic approaches to studying environment and human health: (Forgotten) implications for interdisciplinary research. Environmental Science & Policy 25, 218–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsci.2012.10.015
- Pratschke, J., 2003. Realistic Models? Critical Realism and Statistical Models in the Social Sciences. Philosophica 71, 13–38. https://doi.org/10.21825/philosophica.82236
- Ram, M., Edwards, P., Jones, T., Kiselinchev, A., Muchenje, L., 2015. Getting your hands dirty: critical action research in a state agency [WWW Document]. https://doi.org/10.1177/0950017014523465
- Ritz, B., 2020. Comparing abduction and retroduction in Peircean pragmatism and critical realism [WWW Document]. Routledge, Taylor & Francis Group. URL https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/epdf/10.1080/14767430.2020.1831817?needAccess=true (accessed 12.25.23).
- Robey, D., 1996. Research Commentary: Diversity in Information Systems Research: Threat, Promise, and Responsibility. Information Systems Research 7, 400–408. https://doi.org/10.1287/isre.7.4.400
- Robson, C., 2016. Real world research (4th ed.) - PDF Drive [WWW Document]. pdfdrive. URL http://www.pdfdrive.com/robson-c-et-al-2016-real-world-research-4th-ed-e185336775.html (accessed 12.23.20).
- Saunders, M., Lewis, P., Thornhill, A., 2016. Research Methods for Business Students PDF EBook. Pearson Education, Limited, Harlow, UNITED KINGDOM.
- Sayer, A., 1997. Critical Realism and the Limits to Critical Social Science. Journal for the Theory of Social Behaviour 27, 473–488. https://doi.org/10.1111/1468-5914.00052
- Sayer, A 2004, Why critical realism? in S Fleetwood & S Ackroyd (eds), Critical realist applications in organisation and management studies. Routledge, London, pp. 6-20
- Schostak, J., 2002. Framing the Project: Approaching Qualitative Research in Education (published as: Understanding, Designing and Conducting Qualitative Research in Education ).
- Seuring, S., Gold, S., 2012. Conducting content‐analysis based literature reviews in supply chain management. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal 17, 544–555. https://doi.org/10.1108/13598541211258609
- Shannon-Baker, P., 2016. Making Paradigms Meaningful in Mixed Methods Research. Journal of Mixed Methods Research 10, 319–334. https://doi.org/10.1177/1558689815575861
- Smith, B., Sparkes, A., 2016. Handbook of Qualitative Research in Sport and Exercise.
- Sousa, F., 2010. Meta-Theories in Research: Positivism, Postmodernism, and Critical Realism 16. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1594098
- Thapa, D., Omland, H., 2018. Four steps to identify mechanisms of ICT4D: A critical realism-based methodology. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries 84, e12054. https://doi.org/10.1002/isd2.12054
- Thomas, J., Harden, A., 2008. Methods for the thematic synthesis of qualitative research in systematic reviews. BMC Medical Research Methodology 8, 45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2288-8-45
- Van Maanen, J., 1995. Fear and Loathing in Organization Studies. Organization Science 6, 687–692. https://doi.org/10.1287/orsc.6.6.687
- Williams, C.K., Karahanna, E., 2013. Causal Explanation in the Coordinating Process: A Critical Realist Case Study of Federated IT Governance Structures. MIS Quarterly 37, 933–964.
- Wiltshire, G., 2018. A case for critical realism in the pursuit of interdisciplinarity and impact. Qualitative Research in Sport, Exercise and Health 10, 525–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/2159676X.2018.1467482
- Wong, E., Fui, L., 2012. Pragmatism and critical realism in management research. Actual Problems of Economics 129, 359–364.
- Zachariadis, M., Scott, S., Barrett, M., 2013. Methodological Implications of Critical Realism for Mixed-Methods Research. MIS Quarterly 37, 855–879.