Submission to VIJ 2024-02-15
Keywords
- Tuberculosis, Miliary Tuberculosis, Septic Shock, Metastatic, Sepsis
Copyright (c) 2024 Putra Narendra Ida Bagus

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
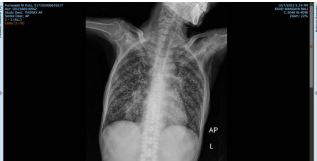
Diagnosing and identifying the underlying disease of septic shock is so difficult, cases of tuberculosis-associated septic shock are extremely rare. A 55-year-old Woman with weakness, nausea, low intake, five episodes of diarrhea, three weeks of coughing, and a positive rapid molecular test result for tuberculosis. The patient had a history of AIDS and was receiving ARV treatment. There had also been a lump in the right neck for a month. A fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) was performed, and the results showed a focus of atypical cells with a background of suppurative chronic inflammation. A physical examination revealed a fever (380C), blood pressure of 78/46 mmHg, and a pulse rate of 110 beats per minute. WBC: 2.60, HB: 7.5, HCT: 23.3, Plt: 353, SGOT/SGPT: 68/8, GDA: 142, BUN/SC: 108/2.6, Na: 141, K: 2.7, Cl: 107 were the results of the laboratory tests. The thorax x-ray revealed a pattern of miliary tuberculosis with a differential diagnosis of the metastatic.
References
- Abdelreheem Y, Mohammad I, Ashraf E, Heba A. Pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with chronic renal failure at Zagazig University Hospitals. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis. 2014; 63(1): p. 187- 192.
- Mohammad A, Ajit S, Ayman K. Tuberculosis in end-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis. International Society for Hemodialysis. 2016; 10(4): p. 360- 364
- Bintcliffe OJ, Lee GY, Rahman NM, Maskell NA. The management of benign non‐infective pleural effusions. Eur Respir Rev. 2016;25:303‐316. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delano MJ, Ward PA: The immune system's role in sepsis progression, resolution, and long-term outcome . Immunol Rev. 2016, 274:330-53. 10.1111/imr.12499
- De Backer D, Orbegozo Cortes D, Donadello K, Vincent JL. Pathophysiology of microcirculatory dysfunction and the pathogenesis of septic shock. Virulence. 2014 Jan 1;5(1):73-9. doi: 10.4161/viru.26482.
- Epidemiology of tuberculosis and progress toward meeting global targets — worldwide, 2019. Fukunaga R, Glaziou P, Harris JB, Date A, Floyd K, Kasaeva T. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:427–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, Osborn TM, Townsend S, Dellinger RP, Artigas A, Schorr C, Levy MM. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: Results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1749–1755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation . The Global Burden of Disease : Generating Evidence, Guiding Policy. https://www.healthdata.org/sites/default/files/files/policy_report/2013/GBD_
- Kethireddy S, Light RB, Mirzanejad Y, et al.: Mycobacterium tuberculosis septic shock. Chest. 2013, 144:474-82. 10.1378/chest.12-1286
- Mayr FB, Yende S, Angus DC. Epidemiology of severe sepsis. Virulence. 2014;5(1):1–11.
- Pavlinac PB, Lokken EM, Walson JL, Richardson BA, Crump JA, John-Stewart GC: Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteremia in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2016, 20:895-902. 10.5588/ijtld.15.0773
- Page MJ, Bester J, Pretorius E: The inflammatory effects of TNF-α and complement component 3 on coagulation. Sci Rep. 2018, 8:1812. 10.1038/s41598-018-20220
- Park EJ, Park MA, Park MJ, Park SY, Lee SH. Corticosteroid therapy for refractory uremic pleurisy. Ewha Med J. 2016;39:125‐128. [Google Scholar]
- PENEFRI. 7th Report Of Indonesian Renal Registry. 2014.Available from: URL: http:// www.indonesianrenalregistry.org.
- Rashid‐Farokhi F, Pourdowlat G, Nikoonia MR, et al. Uremic pleuritis in chronic hemodialysis patients. Hemodial Int. 2013;17:94‐100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray S, Mukherjee S, Ganguly J, Abhishek K, Mitras S, Kundu S. A cross‐sectional prospective study of pleural effusion among cases of chronic kidney disease. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2013;55:209‐213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RISKESDAS (2013). Riset Kesehatan Dasar Indonesia 2013. http://www.depkes.go.id/resources/download/general/HasilRiskesdas2013.pdf
- Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet (London, England). 2020;395(10219):200-11.
- Sanjay G, Manoj K, Chandrakant U. Pleural fluid analysis in pleural effusion patient of chronic kidney disease and non chronic kidney disease: A comparative observational study. MedPulse – International Medical
- Situasi penyakit ginjal kronis.infodatin kementerian kesehatan RI. 2017. ISSN 2442-7659 Journal. 2017; 4(1): p. 2348- 1897.
- Sitifa A, Syaiful A, Mefri Y. Gambaran Klinis Penderita Penyakit Ginjal Kronik yang Menjalani Hemodialisis di RSUP Dr. M. Djamil Padang. Jurnal Kesehatan Andalas. 2018; 7(1): p. 42-50. http://www.usrds.org
- Ulku A, Makbule A, Dilek E, Nagihan K, Erhan O, Ilim I. Role of the Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio in the Differential Diagnosis of Exudative Pleural Effusion. Clinical Sci Journal. 2016; 71(10): p. 611-616.
- U S Renal Data System, USRDS (2013). Annual data report: Atlas of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD.
- Venkatesh M, Arun BS, Suresh H, Sagar Reddy SL. A study of respiratory manifestations in chronic kidney disease. International Journal of Biomedical Research. 2017;8(2):70-4.
- WHO Tuberculosis Fact Sheet. 2015 http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/ http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs104/en/ [Ref list]