Understanding Turnover Intention: Exploring the Influence of Job Security, Perceived Organizational Support, and Job Satisfaction as a Mediator
Submission to VIJ 2023-12-22
Keywords
- Hospitality, Job Satisfaction, Job Security, Perceived Organizational Support, Turnover Intention
Copyright (c) 2023 Diana Nafishah Putri, Fatmah Bagis, Naelati Tubastuvi, Hengky Widhiandono

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Abstract
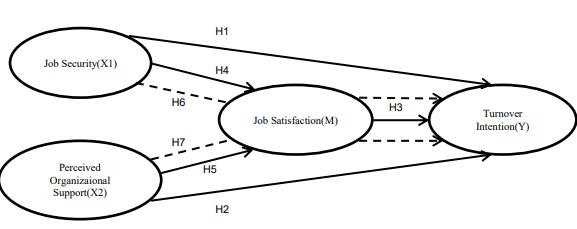
This study aims to examine the effect of independent variables, such as job security and perceived organizational support on the dependent variable, such as turnover intention and job satisfaction as mediation. This study uses a quantitative research design. Distributing questionnaires to employees of 4-star hotels in purwokerto. With a research duration of september-october 2023. The population in this study amounted to 276 employees. The sampling technique used in this study is the quota sampling method according to the proportion of each hotel. calculated using the slovin formula resulted in 176 respondents. the method used to analyze the data is to use smartpls 3.0. In this study, all instruments are valid and reliable. the results showed that job security has no effect on turnover intention. perceived organizational support has no effect on turnover intention. job satisfaction has no effect on turnover intention. job security has a positive and significant effect on job satisfaction. perceived organizational support has a positive and significant effect on job satisfaction. and job satisfaction does not mediate the relationship between job security and perceived organizational support on turnover intention. Job security is able to have a positive and significant influence on employee job satisfaction in 4-star hotels in purwokerto. in addition, organizational support perceived by employees at 4-star hotels in purwokerto can have a significant effect on job satisfaction. however, job satisfaction is not able to mediate the effect of job security and perceived organizational support on employee turnover intention.
References
- Akgunduz, Y., Alkan, C., & Gök, Ö. A. (2018). Perceived organizational support, employee creativity and proactive personality: The mediating effect of meaning of work. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 34, 105–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2018.01.004
- Al-Dalahmeh, M., Héder-Rima, M., & Dajnoki, K. (2020). The effect of talent management practices on employee turnover intention in the information and communication technologies (ICTs) sector: Case of Jordan. Problems and Perspectives in Management, 18(4), 59–71.
- Ali, Z., & Mehreen, A. (2019). Understanding succession planning as a combating strategy for turnover intentions. Journal of Advances in Management Research, 16(2), 216–233. https://doi.org/10.1108/JAMR-09-2018-0076
- Arasanmi, C. N., & Krishna, A. (2019). Employer branding: perceived organisational support and employee retention – the mediating role of organisational commitment. Industrial and Commercial Training, 51(3), 174–183. https://doi.org/10.1108/ICT-10-2018-0086
- Astuti, febriyani dewi, Wulan, heru sri, & Fathoni, A. (2019). organizational commitment, organizational climate, and job security towards turnover intention and job satisfaction as mediating variables at pt. sena garment. Journal of Management, 5(5), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.4213/tmf901
- Atiq, N., & Usmani, S. (2023). Impact of Job Security on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction in the Context of Covid-19 in Pakistan. Pakistan Business Review, 24(4), 347–371. https://doi.org/10.22555/pbr.v24i4.696
- Ayodele, majekodunmi samuel, Abu, Z., & Issa, A. (2022). Job Security Strategy and Job Satisfaction of Non-Teaching Staff in Public Universities in Lagos State. Journal of Strategic Management, 6(3), 21–36. https://doi.org/. https://doi.org/10.53819/81018102t4042
- Ayuningtias, H. G., Shabrina, D. N., Prasetio, A. P., & Rahayu, S. (2019). The Effect of Perceived Organizational Support and Job Satisfaction. 65(Icebef 2018), 691–696. https://doi.org/10.2991/icebef-18.2019.148
- Bagis, F., Darmawan, A., & Ikhsani, M. M. (2021). The effect Of Employee Engagement and Emotional Intelligent on Organizational Commitment by Job Satisfaction as Mediate Variable Case in Employee Of Islamic Education Institution. 7(01), 460–466.
- Bagis, F., Kusumo, U. I., & Hidayah, A. (2021). Job Satisfaction as A Mediation Variable on the Effect of Organizational Culture and Organizational Commitment to Employee Performance. International Journal of Economics, Bussiness and Accounting Research (IJEBAR), 5(2), 424–434.
- Bagis, F., Pratama, B. C., & Kharismasyah, A. Y. (2019). Pengaruh Disiplin Kerja, Komitmen Organisasi Dan Kepuasan Kerja Trhadap Kinerja Karyawan Studi Kasus Institusi Pendidikan. Jurnal Inspirasi Bisnis Dan Manajemen, 3(1), 21.
- Blau, P. (1964). Exchange and power in social life. New York: Wiley.
- Camgoz-Akdag, H., & Zaim, S. (2012). Education: A Comparative Structural Equation Modeling Study. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 874–880. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.750
- Chen, C., & Chen, M. (2021). Hospitality Industry Employees ’ Intention to Stay in Their Job after the COVID-19 Pandemic. Administrative Sciences, 11(144), 1–10. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.3390/admsci11040144
- Crick, A. P., & Spencer, A. (2011). Hospitality quality: New directions and new challenges. International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management, 23(4), 463–478. https://doi.org/10.1108/09596111111129986
- Dhuryana, A. S., & Hussain, F. (2018). The Effecting Job Security and Work Load on Job Satisfaction of Teachers Among Heigher Education Institution in Southern Punjab. 3rd International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering, Management and Scineces, October 2018, 511–518.
- Eisenberger, R., Huntington, R., Hutchison, S., & Sowa, D. (1986). Perceived Organizational Support. 71(3), 500–507.
- Eisenberger, R., Stinglhamber, F., Vandenberghe, C., Sucharski, I. L., & Rhoades, L. (2002). Perceived Supervisor Support : Contributions to Perceived Organizational Support and Employee Retention. 87(3), 565–573. https://doi.org/10.1037//0021-9010.87.3.565
- Ernes, C., F., Y., & Meilani, C. P. (2023). The Effect of Job Security and Burnout on Turnover Intention Mediated by Job Satisfaction. Jurnal Manajemen Kesehatan Indonesia, 11(1), 79–90. https://doi.org/10.21009/ijhcm.05.02.13
- Fadlilah, C. A., & Surjanti, J. (2019). Pengaruh Perceived Organizational Support dan Keadilan Organisasional Terhadap Organizational Citizenship Behavior Melalui Kepuasan Kerja (Studi pada Karyawan PT Purnama Indonesia Sidoarjo). Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen,7(2). 437-446. Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen, 7(2014), 437–446.
- Falahat, M., Gee, S. K., & Liew, C. M. (2019). A model for turnover intention: Banking industry in Malaysia. Asian Academy of Management Journal, 24(November), 79–91. https://doi.org/10.21315/aamj2019.24.s2.6
- Falatah, R., Almuqati, J., Almuqati, H., & Altunbakti, K. (2021). Linking nurses’ job security to job satisfaction and turnover intention during reform and privatization: A cross-sectional survey. Journal of Nursing Management, 29(6), 1578–1586. https://doi.org/10.1111/jonm.13279
- Firdaus, F., & Lusiana, H. (2020). Pengaruh Komitmen Organisasi Dan Kepuasan Kerja Terhadap Turnover Intention. At-Tadbir : Jurnal Ilmiah Manajemen, 4(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.31602/atd.v4i1.1874
- Ganji, S. F. G., Johnson, L. W., Sorkhan, V. B., & Banejad, B. (2021). The effect of employee empowerment, organizational support, and ethical climate on turnover intention: The mediating role of job satisfaction. Iranian Journal of Management Studies, 14(2), 311–329. https://doi.org/10.22059/IJMS.2020.302333.674066
- Giao, H. N. K., Vuong, B. N., Huan, D. D., Tushar, H., & Quan, T. N. (2020). The effect of emotional intelligence on turnover intention and the moderating role of perceived organizational support: Evidence from the banking industry of vietnam. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(5), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12051857
- Gom, D., Lew, T. Y., Jiony, M. M., Tanakinjal, G. H., & Sondoh, S. (2021). The Role of Transformational Leadership and Psychological Capital in the Hotel Industry : A Sustainable Approach to Reducing Turnover Intention.
- Guberina, T., & Min Wang, A. (2021). Entrepreneurial Leadership Impact on Job security and Psychological Well-being during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A conceptual review. International Journal of Innovation and Economic Development, 6(6), 7–18. https://doi.org/10.18775/ijied.1849-7551-7020.2015.66.2001
- Guzeller, C. O., & Celiker, N. (2020). Examining the relationship between organizational commitment and turnover intention via a meta-analysis. International Journal of Culture, Tourism, and Hospitality Research, 14(1), 102–120. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJCTHR-05-2019-0094
- Hair, J. F., Anderson, R. E., Tatham, R. L., & Black, W. C. (1998). Multivariate Data Analysis (5th ed). Prentice Hall.
- Hasan, A., Noreen, S., & Hafeez, M. (2018). The Relationship among Perceived Organizational Support, Trust, Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention: A Study of Banking Sector in Pakistan. International Journal of Human Resource Studies, 8(4), 227. https://doi.org/10.5296/ijhrs.v8i4.13686
- Hayati, N. (2020). Pengaruh Persepsi Dukungan Organisasi Dan Budaya Organisasi Terhadap Organizational Citizenship Behaviour Melalui Kepuasan Kerja. Equilibrium: Jurnal Ekonomi, Manajemen, Akuntansi, 16(2), 54–61.
- Herianto, F., & Yanuar, Y. (2021). Pengaruh Perceived Organizational Support Terhadap Turnover Intention Dengan Job Satisfaction Sebagai Variabel Mediasi Pada PT. BANK MNC DI JAKARTA PUSAT. Jurnal Manajerial Dan Kewirausahaan, 3(1), 82. https://doi.org/10.24912/jmk.v3i1.11290
- Herzberg. (1968). One more time: How do you motivate employees.
- Homans, G. C. (1958). Social Behavior As Exchange. American Journal of Sociology, 63(6), 597–606.
- Islamiyati, H., & Sahrah, A. (2022). Relationship Between Perceived Organizational Support With Turnover Intention In Female Employees. Journal of Psychological Perspective, 4(2), 53–58. https://doi.org/10.47679/jopp.423332022
- Jaelani, D., & Desiani, R. (2022). The Effect of Work Stress Job Satisfaction and Organizational Climate on Turnover Intention (Survey on Employees of PT. Allied Industrial Indonesia). Portofolio: Jurnal Ekonomi, Bisnis, Manajemen, Dan Akuntansi, 17(1), 30–45. https://doi.org/10.54783/portofolio.v17i1.193
- Jing, J., & Yan, J. (2022). Study on the Effect of Employees’ Perceived Organizational Support, Psychological Ownership, and Turnover Intention: A Case of China’s Employee. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 19(10). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19106016
- Kansakar, P., Munir, A., & Shabani, N. (2019). Technology in the Hospitality Industry: Prospects and Challenges. IEEE Consumer Electronics Magazine, 8(MAy), 60–65. https://doi.org/10.1109/MCE.2019.2892245
- Karaalioglu, Z. F., & Karabulut, A. T. (2019). the Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction on the Relationship Between Perceived Organizational Support and Job Performance. Business & Management Studies: An International Journal, 7(2), 1022–1041. https://doi.org/10.15295/bmij.v7i2.1119
- Khawrin, M. K., & Sahibzada, A. (2023). The mediating role of job satisfaction at selected public universities in Afghanistan: the effect of job security on turnover intention. Journal of Management and Business Education, 6(3), 244–256. https://doi.org/10.35564/jmbe.2023.0013
- Kim, M. J., & Kim, B. J. (2020). Analysis of the importance of job insecurity, psychological safety and job satisfaction in the CSR-performance link. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(9), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/SU12093514
- Kurniawan, R., & Sutiyanti. (2021). Pengaruh Motivasi, Pelatihan Dan Disiplin Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Pada Hotel Berbintang Di Kota Batam. Conference on Management, Business, Innovation, Education and Social Science, 1(1), 457–467. https://journal.uib.ac.id/index.php/combines/article/view/4471%0Ahttps://journal.uib.ac.id/index.php/combines/article/download/4471/1188
- Lubis, F., & Nurhayati, M. (2020). the effect of perceived organizational support and workload on job satisfaction through work-school conflict as a mediating variable. 1(3), 277–293. https://doi.org/10.31933/DIJMS
- Maan, A. T., Abid, G., Butt, T. H., Ashfaq, F., & Ahmed, S. (2020). Perceived organizational support and job satisfaction: a moderated mediation model of proactive personality and psychological empowerment. Future Business Journal, 6(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43093-020-00027-8
- Maqableh, O., Helalat, A., & Nor, C. S. M. (2023). “Exploring the mediating influence of job satisfaction on the relationship between job security and turnover intention: A case study of the hospitality industry of Jordan.” Problems and Perspectives in Management, 21(1), 384–395. https://doi.org/10.21511/ppm.21(1).2023.33
- Maulidah, K., Ali, S., & Pangestuti, D. C. (2022). Pengaruh Beban Kerja dan Kepuasan Kerja terhadap Turnover Intention Karyawan RSU “ABC” Jakarta Selatan. Jurnal Akuntansi, Keuangan, Dan Manajemen, 3(2), 159–176. https://doi.org/10.35912/jakman.v3i2.611
- Mcmillan, rita clay. (1997). Customer satisfaction and organizational support for service providers. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.050
- Meltz, N. M. (2005). Job Security in Canada. Relations Industrielles, 44(1), 149–161. https://doi.org/10.7202/050477ar
- Murdani, A. A., & Fachrurrozie, F. (2022). Pengaruh Kepuasan Kerja Dan Komitmen Organisasi Terhadap Turnover Intention Auditor. Jurnal JAEMB, 2(1), 56–63.
- Nassani, A. A., & Aljarallah, K. A. (2023). The Impact of Organizational Support and Ethical Climate On Turnover Intention : Job Satisfaction as a Mediator. 43(3), 227–238. https://doi.org/10.21608/AJA.2022.140340.1252
- Nemteanu, M. S., Dinu, V., & Dabija, D. C. (2021). Job insecurity, job instability, and job satisfaction in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Journal of Competitiveness, 13(2), 65–82. https://doi.org/10.7441/JOC.2021.02.04
- O’Connor, J. (2018). The impact of job satisfaction on the turnover intent of executive level central office administrators in texas public school districts: A quantitative study of work related constructs. Education Sciences, 8(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci8020069
- Pariyanti, E., Rinnanik, R., & Mardiono, T. (2019). Pengaruh Motivasi Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Karyawan Dengan Kepuasan Kerja Sebagai Variabel Intervening Pada PT. Federal International Finance (FIF). Relasi : Jurnal Ekonomi, 15(2), 293–307. https://doi.org/10.31967/relasi.v15i2.313
- Park, J., & Min, H. (Kelly). (2020). Turnover intention in the hospitality industry: A meta-analysis. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 90(May 2019), 102599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102599
- Parwita, gde bayu surya, Suryani, ni nyoman, & Adriani, ni komang ayu. (2019). Kepuasan Kerja dan Komitmen Organisasi Pengaruhnya Terhadap Turnover Intention pada CV. Dwi Boga Utama. Forum Manajemen, 17, 87–96.
- Popa, I., Lee, L., Yu, H., & Madera, J. M. (2023). Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management Losing talent due to COVID-19 : The roles of anger and fear on industry turnover intentions. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 54(December 2022), 119–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2022.12.010
- Putranti, H. R. D., Suparmi, S., & Suprapti, S. (2021). Analisis Perceived Organizational Support, Quality Culture, dan Kepuasan Kerja sebagai Second-Order Factor terhadap Turnover Intention Karyawan Generasi Y di ATC (Air Traffic Control). Jurnal Maksipreneur: Manajemen, Koperasi, Dan Entrepreneurship, 10(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.30588/jmp.v10i2.765
- Rachmandha, A. A., & Husniati, R. (2022). Pengaruh Kepuasan Kerja, Pengembangan Karir, Dan Lingkungan Kerja Terhadap Turnover Intention Di PT XYZ. Jap, 22(22), 1–13.
- Rahman, S. M. (2020). Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention: Evidence from Bangladesh. Asian Business Review, 10(2), 99–XX. https://doi.org/10.18034/abr.v10i2.470
- Rathakrishnan, T., Imm, N. S., & Kok, T. K. (2016). Turnover intentions of lecturers in private universities in Malaysia. Pertanika Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 24(November), 129–146.
- Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2017). Organizational Behaviour (16th ed.). Salemba Empat.
- Romeo, M., Yepes-Baldó, M., & Lins, C. (2020). Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intention Among People With Disabilities Working in Special Employment Centers: The Moderation Effect of Organizational Commitment. Frontiers in Psychology, 11(June), 1–8. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01035
- Rozana, M., & Dwiyanti, R. (2022). Peran Perceived Organizational Support Terhadap Turnover Intentions. Psimphoni, 1(2), 2775–1805.
- Shabannia Mansour, M., & Hassan, K. H. (2019). Job Security and Temporary Employment Contracts in Islamic Jurisprudence. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-92114-3_4
- Shafique, I., N. Kalyar, M., & Ahmad, B. (2018). The Nexus of Ethical Leadership, Job Performance, and Turnover Intention: The Mediating Role of Job Satisfaction. Interdisciplinary Description of Complex Systems, 16(1), 71–87. https://doi.org/10.7906/indecs.16.1.5
- Sokhanvar, M., Kakemam, E., Chegini, Z., & Sarbakhsh, P. (2018). Hospital nurses’ job security and turnover intention and factors contributing to their turnover intention: A cross-Sectional study. Nursing and Midwifery Studies, 7(3), 133. https://doi.org/10.4103/nms.nms_2_17
- Srivastava, S., & Agrawal, S. (2020). Resistance to change and turnover intention: a moderated mediation model of burnout and perceived organizational support. Journal of Organizational Change Management, 33(7), 1431–1447. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOCM-02-2020-0063
- Stater, K. J., & Stater, M. (2019). Is It “Just Work”? The Impact of Work Rewards on Job Satisfaction and Turnover Intent in the Nonprofit, For-Profit, and Public Sectors. American Review of Public Administration, 49(4), 495–511. https://doi.org/10.1177/0275074018815261
- Suliyanto, P. (2018). Metode Penelitian Bisnis untuk Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi. Yogyakarta, Andi Publisher.
- Tambun, S., Laura, N., Lukiyana, & Prakashita, V. (2019). Pengaruh Perceived Organizational Support Dan Job Satisfaction Terhadap Turnover Intention Melalui Komitmen Organisasi Sebagai Pemoderasi. Media Manajemen Jasa, 7(2), 1–17.
- Tampubolon, V. S., & Sagala, E. J. (2020). Pengaruh Kepuasan Kerja Dan Komitmen Organisasi Terhadap Turnover Intention Pada Karyawan Pt. Bum Divisi Pmks. Business Management Journal, 16(2), 65. https://doi.org/10.30813/bmj.v16i2.2359
- Tett, R. P., & Meyer, J. P. (1993). Job Satisfction, Organizational Commitment, Turnover Intention, and Turnover: PAth Analyses Based On Meta-analytic findings.
- Umrani, W. A., Afsar, B., Khan, M., & Ahmed, U. (2019). Addressing the issue of job performance among hospital physicians in Pakistan: The role of job security, organizational support, and job satisfaction. Journal of Applied Biobehavioral Research, 24(3), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/jabr.12169
- Wang, H., Ma, B., Liu, X., & Liu, S. (2014). Job security and work outcomes in China: Perceived organizational support as mediator. Social Behavior and Personality, 42(7), 1069–1076. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2014.42.7.1069
- Wang, Q., & Wang, C. (2020). Reducing turnover intention: perceived organizational support for frontline employees. Frontiers of Business Research in China, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s11782-020-00074-6
- Wen, J., Huang, S. (Sam), & Hou, P. (2019). Emotional intelligence, emotional labor, perceived organizational support, and job satisfaction: A moderated mediation model. International Journal of Hospitality Management, 81(July 2017), 120–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.01.009